Bio-inspired Algorithms
For some reason, that I still don’t know, I noticed a interest to read about Bio-Inspired Algorithms (Natural Computing).
Natural Computing is when nature is the source of inspiration to development of new computer techniques. We have three groups.
- Nature inspired computing
- Evolutionary Computing
- Collective Intelligence
- Artificial neural networks
- Artificial Immunological Systems
- Simulation of natural events
- Fractals
- Artificial Life
- Flights simulators
- Computing using natural media
- Quantum Computing
- DNA-based computing
But what I will write about is
Bio-inspired Algorithms
Inside Nature inspired computing area we have somes algorithms categories:
- Neural Netorks
- MLP – Multi-layer Perceptrons
- RBF- Radio Basis Function Net
- SOM- Self-Organizing Maps
- ARTMap
- Evolutionary algorithm
- Genetic algorithm
- Genetic programming
- Grammatical evolution
- Evolutionary strategy
- Evolutionary programming
- Collective Intelligence
- Ants colony
- Particle swarm optimization (PSO)
- Artificial Immunological Systems
- Negative Selection Algorithm
- Clonal Selection Algorithm
- Immune Network Algorithms
- Dendritic Cell Algorithms
Artificial Immunological Systems
Not Finished
Collective Intelligence
Collective intelligence is shared or group intelligence that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making.

Not Finished
Neural Networks
Neurons communicate through synapses. Synapse is the region where two neurons come into contact and through which the nerve impulses are transmitted between them. The impulses received by a neuron A at a given moment are processed and at a given threshold of action, neuron A triggers, producing a neurotransmitter substance that flows from the cell body to the axon, which may be connected to a dendrite of another neuron B. The neurotransmitter may decrease or increase the polarity of the postsynaptic membrane by inhibiting or exciting the generation of pulses in neuron B. This process depends on several factors, such as the synapse geometry and the type of neurotransmitter.
On average, each neuron forms between a thousand and ten thousand synapses. The human brain has about 10 E11 neurons, and the number of synapses is more than 10 E14, making possible the formation of very complex networks.
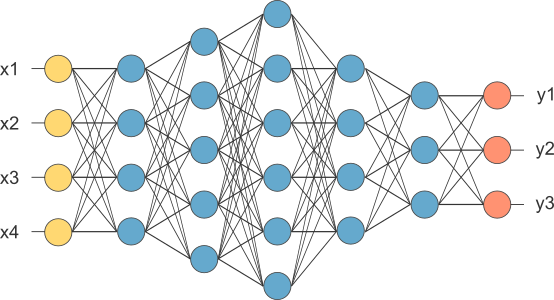
In artificial neural networks we have 3 main kinds of neurons layers:
- Input layer: Where the patterns are presented to net.
- Hidden layers: Where the processing happens through weighted connections.
- Output layer: Where final result is presented.
Learning Process
ANN has the property of learning of its environment and improve its performance through the process of the training (iterative process of adjustment of weights). Learning occurs when the neural network reaches a generalized solution to a class of problems. There are several learning algorithms specific to certain models of neural networks, these algorithms differ mainly by the way the weights are modified. Another important factor is the way in which a neural network relates to the environment. In this context there are the following learning paradigms:
- Supervised Learning: an external agent indicates to network the expected response to the input pattern;
- Non-Supervised Learning (self-organization): there is no external agent;
- Reinforcement: when an external critic evaluates the response provided by the network.
Training is the execution of all cycles (pairs of inputs and outputs) of the training set. The correction of weights in a cycle can be performed in two ways:
- Standard Mode: Correction happens with each presentation of an input and output. N corrections occur in each cycle.
- Batch Mode: Correction occurs due to the average error resulting from the display of all inputs and outputs of the cycle. Only one correction is made per cycle.
Evolutionary Algorithm
An evolutionary algorithm is subset of evolutionary computing characterized by ‘selection’, ‘recombination’ and ‘mutation’ of populations. These algorithms are typically stochastic and can be implemented with the following steps:
- Generate an initial population (eg randomly)
- Evaluate the fitness of each individual
- Repeat the steps until the end:
- Select the best-fit individuals for reproduction. (Parents)
- Breed new individuals through crossover and mutation operations to give birth to offspring.
- Evaluate the individual fitness of new individuals.
- Replace least-fit population with new individuals.
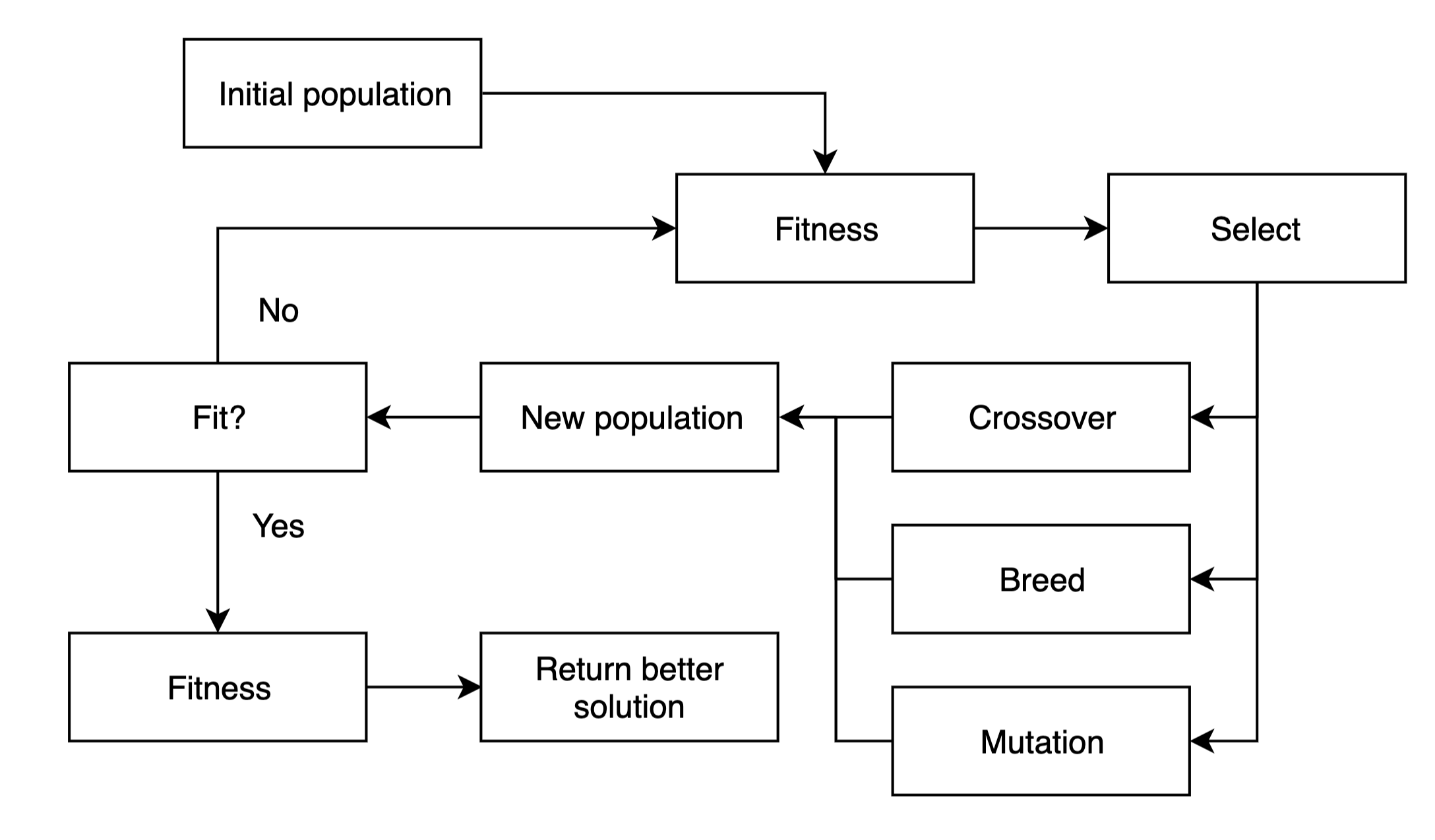
Even though theses algorithms don’t guarantee that the optimal solution will be found, but rather the near-optimal,differnts strategies to use algorithm evolutionary associated to differntes numeric representation. For example: bits array is used to genetic algorithm, reals array is used to evolutionary strategy, finite state machine is used to volutionary programming and threes is used to genetic programming. This algorihms solve a very popular problem of travelling salesman.